

Mendeleev had said that the properties of elements vary in a regular, predictable pattern when the elements are arranged according to their atomic masses. Moseley ’s discovery made possible a new understanding of the periodic law first proposed by Dmitri Mendeleev in the late 1850s.

Moseley hypothesized that the regular change in wavelength from element to element was caused by an increase in the positive charge on atomic nuclei in going from one element to the next-heavier element. He discovered that the wavelength of the reflected x rays decreased in a regular predictable pattern with increasing atomic mass. Moseley bombarded a number of chemical elements with x rays and observed the pattern formed by the reflected rays. The concept of atomic number evolved from the historic research of Henry Gwyn-Jeffreys Moseley in the 1910s. Accordingly the atomic number is often omitted from a nuclear symbol, as in 16O, where the superscript represents the atomic mass (a attribute than does vary with isotopes of an element). In nuclear chemistry, an element ’s atomic number is written to the left and below the element ’s symbol The number of protons for a particular element never varies, if one changes the number of protons one is changing the element. It is always the smaller whole number found in association with an element ’s symbol in the table. The atomic number of an element can be read directly from any periodic table. Since each proton carries a single positive charge, the atomic number is also equal to the total positive charge of the atomic nucleus of an element.
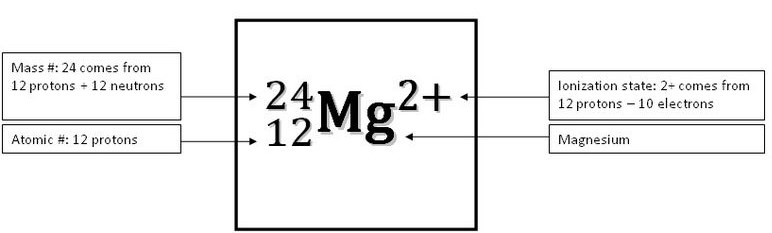
Oxygen ’s atomic number is, therefore, eight. For example, the nucleus of an oxygen atom contains eight protons and eight neutrons. The universe began with simple elements like hydrogen and helium that under high heat and pressure were forced together binding their protons and neutrons with a strong nuclear force.The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of its atom. Under these conditions it is possible to undergo nuclear fusion, adding nucleuses together to increase the number of protons and neutrons. This is a natural phenomenon, when the universe first began stars were areas of high gravity, heat and force. This is because a proton is added to the nucleus each time. This means as we progress along a period (from side to side) or down a group (up and down) the atoms get progressively larger usually by a unit of one. And as you progress down the periodic table the atomic numbers also increase. A key trend in the periodic table is its ascending number of protons from left to right, going across the periods. This difference in the number of protons means not only are they different elements but they are at different places in the periodic table. For example, Carbon has 6 protons and Chlorine has 17. This is what determines what element it is.

has one proton in the nucleus and would have a mass of 1.672622x10-27 Kg.Įvery element has a different number of protons in the nucleus. If we looked at the atomic mass of Beryllium considering the real mass of a proton (1.672622x10-27 Kg) the actual atomic mass would be 9.012182 x10 -27 Kg when considering the mass of protons in Kg. mass of 1.įor example the atomic number of Beryllium is 4 as it has 4 protons in the nucleus each worth a mass unit of 1. As we say that a proton has a mass of 1 for every proton we have in the nucleus this corresponds to an increase in a. The atomic number of an element links back to the mass of a proton. Dimitri Mendeleev initially began by structuring the periodic table based on the different elements' chemical properties, much as it still is today but a key concept underpinning the periodic table is Atomic Number. The periodic table as laid out by Dimitri Mendeleev, the founding father of the periodic table is based on a key concept that everything relates to the mass of the atom.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
